Health Promotion and Disease Prevention: An Overview of the Process

Both health promotion and disease prevention focus on better outcomes and quality of life, and in most cases, both are uses simultaneously to promote a healthy individual and community. However, the difference is when the focus is carried out. Health promotion engages and empowers individuals and communities to choose healthy behaviors and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases through primary prevention. In contrast, disease prevention focuses on reducing chronic diseases’ development and severity through secondary and tertiary prevention. There are considerable risk factors for disease, or the disease process has already begun.
The Role of Health Promotion
Health promotion practices have evolved in response to the rising rates of chronic disease. Programs are being developed with a multidisciplinary team approach that helps find the right path for individualized health promotion. By focusing on improving individuals, families, and communities’ health status, we can improve our quality of life.
Risk Factor Reduction and Disease Prevention
Modifiable risk factors are responsible for 75% of chronic diseases and 75% of healthcare costs. By managing the diet, physical activity, smoking cessation, avoiding excessive alcohol, and other modifiable risk factors, we can improve our health and decrease risks for chronic disease and premature deaths.
Determination of Health
What makes some people healthy and others not? How can we create a society in which everyone has a chance to live a long healthy life? Healthy People 2020 has set out to explore these questions. They have developed objectives that address the relationship between health status and biology, individual behavior, health services, social factors, and policies. The objectives have an emphasis on the ecological approach to disease prevention and health promotion. The ecological approach focuses on both individual-level and population-level determinants of health and interventions.
The range of personal, social, economic, and environmental factors that influence health status is known as health determinants.
The 5 Major Determinants of Health
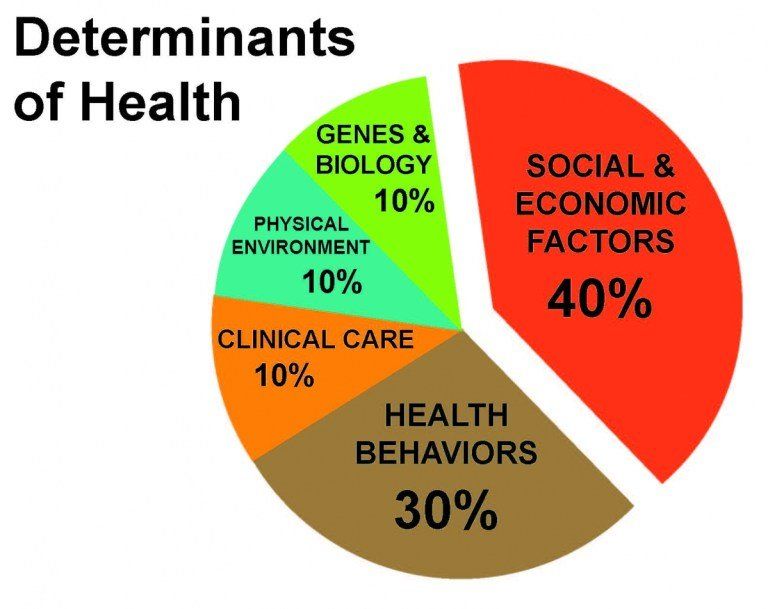
Health promotion and disease prevention take a multifaceted approach: it involves community and self-preservation. The idea of wellness and application has multiple parts that require direct self-control and adherence to direct regimens of monitoring self-behaviors, dietary practices, and indirect regimens as in elected officials and laws put into place to promote wellness in the community and environment.
Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Programs
Healthcare programs that have a primary focus on specific efforts aimed at reducing the development and severity of chronic disease and other morbidities.
The programs are designed to help clients achieve and continue to enjoy optimal health. Your program director will design programs that will:
- Help clients identify the target state.
- Help clients discover their strengths and needs.
- Support path to full health and wellness potential.
Application of Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
3 Strategies of Health Promotion
- Enabling: This includes a secure foundation in a supportive environment, access to information, life skills, and opportunities for making healthy choices. People cannot achieve their fullest health potential unless they can take control of those things that determine their health. This must apply equally to women and men.
- Mediating: Professional and social groups and health personnel have a major responsibility to mediate between differing interests in society to pursue health.
- Advocacy: Good health is a major resource for social, economic, and personal development and an important dimension of life quality. Political, economic, social, cultural, environmental, behavioral, and biological factors can favor health or be harmful. Health promotion action aims at making these conditions favorable through advocacy for health.
5 Principals for Health Promotion
- A broad and positive health concept
- Participation and involvement
- Action and action competence
- Setting perspective
- Equity in health
Prevention
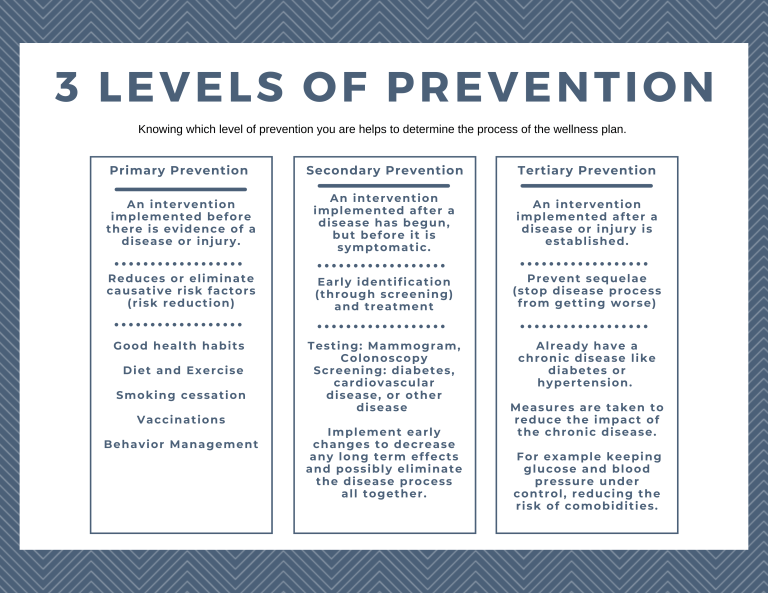
The Aim of A Wellness Program
Wellness programs are designed to engage and empower individuals and communities to choose healthy behaviors and make changes that reduce the risk of developing a chronic disease or other morbidities while enabling people to increase control over their own health.
Wellness programs pull together community resources to support, train and encourage clients to pursue well-being in all dimensions of a person’s life, including: social, environmental, occupational, intellectual, emotional, and spiritual.
References
https://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/about/foundation-health-measures/Determinants-of-Health
https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/index.htm
https://www.who.int/teams/health-promotion/enhanced-wellbeing/first-global-conference
Kumar, S., & Preetha, G. (2012). Health promotion: an effective tool for global health. Indian journal of community medicine : official publication of Indian Association of Preventive & Social Medicine, 37(1), 5–12. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-0218.94009
National Research Council (US) Panel on Statistics for an Aging Population; Gilford DM, editor. The Aging Population in the Twenty-First Century: Statistics for Health Policy. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1988. 5, Health Promotion and Disease Prevention. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK217727/




